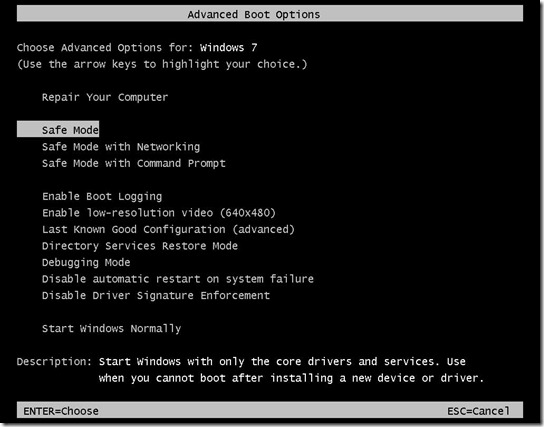
Run Windows Service as a console program. Posted: 2. 00. 7- 0. Last updated: 2. 01. Visual Studio and the .
NET framework make it really easy to create Windows Services. All you have to do is create a new project, select . However, debugging Windows Services in Visual Studio can be a big pain. The recommended way is to use Install.
Util to install them, and then restart the service and attach the debugger everytime you want to debug it. I wanted Windows Live! Bot to be available as a Windows Service, but I also wanted to be able to debug it without the hassle, so here's what I came up with. System. Service. Process. Demo. Service : Service.
This article helps in running the Windows Service in debug mode so that we can debug the service to check the flow of code or fixing any of the issues. Targets with tags=. Specify such test targets with explicit labels on the command line if. How do I start a service with certain parameters? In another question I have found net start servicename blah but if I try this, net throws a syntax error at me. Microsoft Windows services, formerly known as NT services, enable you to create long-running executable applications that run in their own Windows sessions.
Base. . What it does is in the Main method it checks the . This will be true when it is run from Visual Studio, or when you just click on the . When it's run from Visual Studio or as a standalone program it will keep running until you press a key, then it will call your On. Stop method and then terminate. Two things to watch out for: You'll have to right click on your project in Visual Studio, choose Properties and select the Output type as .

I'm sure there are a few things different between Windows Services and console programs that I don't know about, and might make the console version of the program behave strangely in some cases. It has also been pointed out that there is no way to test pause- and- resume in the console version. The best way I could think of to mimic service events like these would be to read in keypresses in the main thread and do the appropriate action depending on the key pressed. For instance, instead of the . However, I don't have the time and interest to do it right now, so implementing it is left as an exercise for the reader : ).
DB2 9.7 APAR Fix list contains list of APARs shipped for each fix pack in DB2 Version 9.7 for Linux, UNIX and Windows products. The Severity column value of 1 is high. Key Windows XP Executables. The range and number of files included in the Windows XP folder structure are enormous. Most of these files are drivers, DLLs, or some.
Command- Line Options - Troubleshooting Guide for Java SE 6 with Hot. Spot VMAppendix B. This section describes some command line options that can be useful in diagnosing problems. B. 1 Hot. Spot VM Command- Line Options. Command- line options that are prefixed with - XX are specific to the Java Hot. Spot Virtual Machine.
Many of these options are important for performance tuning and diagnostic purposes, and are therefore described in this appendix. All the - XX options are described here. B. 1. 1 Dynamic Changing of Flag Values. With the jinfo - flag command ( 2.
Utility ) and with the JConsole utility ( 2. JConsole Utility), you can dynamically set, unset, or change the value of certain Java VM flags for a specified Java process. For the complete list of these flags, use the MBeans tab of the JConsole utility. Armies Of Exigo Download Crack Gta. See the list of values for the Diagnostic.
Options attribute of the Hot. Spot. Diagnostic MBean, which is in the com. These flags are the following: Heap.
Dump. On. Out. Of. Memory. Error. Heap. Dump. Path. Print. GCPrint. GCDetails. Print. GCTime. Stamps. Print. Class. Histogram.
Print. Concurrent. Locks. B. 1. 2 - XX: +Heap. Dump. On. Out. Of. Memory. Error Option. The - XX: +Heap.
Dump. On. Out. Of. Memory. Error command- line option tells the Hot. Spot VM to generate a heap dump when an allocation from the Java heap or the permanent generation cannot be satisfied.
There is no overhead in running with this option, and so it can be useful for production systems where Out. Of. Memory. Error takes a long time to surface. You can also specify this option at runtime with the MBeans tab in the jconsole utility. The heap dump is in HPROF binary format, and so it can be analyzed using any tools that can import this format. For example, the jhat tool can be used to do rudimentary analysis of the dump.
See 2. 5 jhat Utility . The following example shows the result of running out of memory with this flag set. When java. lang.
Out. Of. Memory. Error is thrown, a heap dump file is created. In this case the file is 5. MB and is created as java.
You can specify an alternative file name or directory with the - XX: Heap. Dump. Path= option. For example - XX: Heap. Dump. Path=/disk. B. 1. 3 - XX: On. Error= Option. When a fatal error occurs, the Hot. Spot Virtual Machine can optionally execute a user- supplied script or command.
The script or command is specified using the - XX: On. Error=string command line option, where string is a single command, or a list of commands separated by a semicolon.
Within string, all occurrences of %p are replaced with the current process ID (pid), and all occurrences of %% are replaced by a single %. The following examples demonstrate how this option can be used. On Solaris OS the pmap command displays information about the address space of a process. In the following example, if a fatal error occurs, the pmap command is executed to display the address space of the process.
In the following example, the gcore command is executed to create the core image, and the debugger is started to attach to the process. Once launched, gdb will attach to the VM process java - XX: On. Error=. Watson debugger can be configured as the post- mortem debugger so that a crash dump is created when an unexpected error is encountered. See 7. 4. 4 Collecting Crash Dumps on Windows for other details. An alternate approach to obtaining a crash dump on Windows it to use the - XX: On. Error option to execute the userdump. See 7. 4. 4 Collecting Crash Dumps on Windows for further details.
The above example assumes that the path to the userdump. PATH variable. B. XX: +Show. Message. Box. On. Error Option. When the option - XX: +Show.
Message. Box. On. Error is set and a fatal error is encountered, the Hot.
Spot VM will display information about the fatal error and prompt the user to specify whether the native debugger is to be launched. In the case of Solaris OS and Linux, the output and prompt are sent to the application console (standard input and standard output). In the case of Windows, a Windows message box pops up. Below is an example from a fatal error encountered on a Linux system. If the user enters y or yes, gdb will be launched (assuming it is on the PATH variable). On Solaris OS the message is similar to the above except that the user is prompted to start the dbx debugger.
On Windows a message box is displayed. If the user presses the YES button, the VM will attempt to start the default debugger. This debugger is configured by a registry setting; see 7. Collecting Crash Dumps on Windows for further details.
If Microsoft Visual Studio is installed, the default debugger is typically configured to be msdev. In the above example the output includes the process ID (1. ID (1. 02. 6 in this case). If the debugger is launched, one of the initial steps in the debugger might be to select the thread and obtain its stack trace.
As the process is waiting for a response it is possible to use other tools to obtain a crash dump or query the state of the process. On Solaris OS, for example, a core dump can be obtained using the gcore utility. On Windows a Dr. Watson crash dump can be obtained using the userdump or windbg programs. The windbg program is included in Microsoft's Debugging Tools for Windows. See 7. 4. 4 Collecting Crash Dumps on Windows for further information on windbg and the link to the download location. In windbg select the Attach to a Process menu option, which displays the list of processes and prompts for the process ID.
The Hot. Spot VM displays a message box, which includes the process ID. Once selected the . In the following example a crash dump is created in file crash. Creating Crash Dump with windbg. In general the - XX: +Show. Message. Box. On. Error option is more useful in a development environment where debugger tools are available.
The - XX: On. Error option is more suitable for production environments where a fixed sequence of commands or scripts are executed when a fatal error is encountered. B. 1. 5 Other - XX Options. Several other - XX command- line options can be useful in troubleshooting.- XX: On. Out. Of. Memory. Error=string is used to specify a command or script to execute when an Out. Of. Memory. Error is first thrown.- XX: Error. File=filename is used to specify a location for the fatal error log file.
See C. 1 Location of Fatal Error Log.- XX: Heap. Dump. Path=path is used to specify a location for a heap dump. See B. 1. 2 - XX: +Heap.
Dump. On. Out. Of. Memory. Error Option .- XX: Max. Perm. Size=size is used to specify the size of the permanent generation memory. See 3. 1. 2 Detail Message: Perm. Gen space.- XX: +Print. Command. Line. Flags is used to print all the VM command- line flags. See 7. 3 Collecting Data for a Bug Report.- XX: +Print.
Concurrent. Locks will cause the Ctrl- Break handler to print a list of concurrent locks owned by each thread.- XX: +Print. Class. Histogram will cause the Ctrl- Break handler to print a heap histogram.- XX: +Print. GCDetails and - XX: +Print.
GCTime. Stamps are used to print detailed information about garbage collection. See B. 2. 3 - verbose: gc Option .- XX: +Use.
Alt. Sigs is used (on Solaris 8 and 9 OS) to instruct the Hot. Spot VM to use alternate signals to SIGUSR1 and SIGUSR2.
See 6. 1 Signal Handling on Solaris OS and Linux.- XX: +Use. Conc. Mark. Sweep. GC, - XX: +Use. Serial. GC, and - XX: +Use. Parallel. GC specify the garbage collection policy to be used. See 4. 2. 2 Crash During Garbage Collection.
B. 2 Other Command- Line Options. In addition to the - XX options, many other command- line options can provide troubleshooting information. This section describes a few of these options. B. 2. 1 - Xcheck: jni Option. The - Xcheck: jni option is useful in diagnosing problems with applications that use the Java Native Interface (JNI). Sometimes bugs in the native code can cause the Hot. Spot VM to crash or behave incorrectly.
The - Xcheck: jni option is added to the command line that starts the application, as in the following example. Note that the option is not guaranteed to find all invalid arguments or diagnose logic bugs in the application code, but it can help diagnose a large number of such problems. When an invalid argument is detected, the VM prints a message to the application console or to standard output, prints the stack trace of the offending thread, and aborts the VM. In the following example, a NULL value was incorrectly passed to a JNI function that does not allow a NULL value. There is one exception to this behavior. When a JNI call is made within a JNI critical region, the following non- fatal warning message is printed. The reference is held until the native code calls the corresponding release function.
The code between the get and release is called a JNI critical section and during that time the Hot. Spot VM cannot bring the VM to a state that allows garbage collection to occur. The general recommendation is not to use other JNI functions within a JNI critical section, and in particular any JNI function that could potentially cause a deadlock. The warning printed above by the - Xcheck: jni option is thus an indication of a potential issue; it does not always indicate an application bug.
For more information on JNI, refer to the Java Native Interface documentation web site. B. 2. 2 - verbose: class Option.
The - verbose: class option enables logging of class loading and unloading. B. 2. 3 - verbose: gc Option.
The - verbose: gc option enables logging of garbage collection (GC) information. It can be combined with other Hot. Spot VM specific options such as - XX: +Print.
News
- Cardcaptor Sakura Mugen Character Download Monkey
- Adobe Reader Download Button Missing In Yahoo
- International Express Pre Intermediate Workbook Download Music
- Download Pes 2012 Full Version Free For Pc Crack
- Ip Hack Pro By Black Boy Sparknotes
- Lancinho Turma Do Pagode Baixar Gratis
- Download Free Truecaller Software For Java Phones
- Windows Vista Windows 7 Crack Activators Only
- Install Os On Esata Drive Dock
- Vipre Antivirus 2012 5 0 Crack Instructions For Schedule
- Si Me Muero Manana Nejo Download Free
- Hkey_Current_User Software Adobe Acrobat Distiller Printerjobcontrol
- Microsoft Access 2003 Full Outer Join Oracle